azure-notes
Use Managed Identities in App Service with HTTP REST Protocol
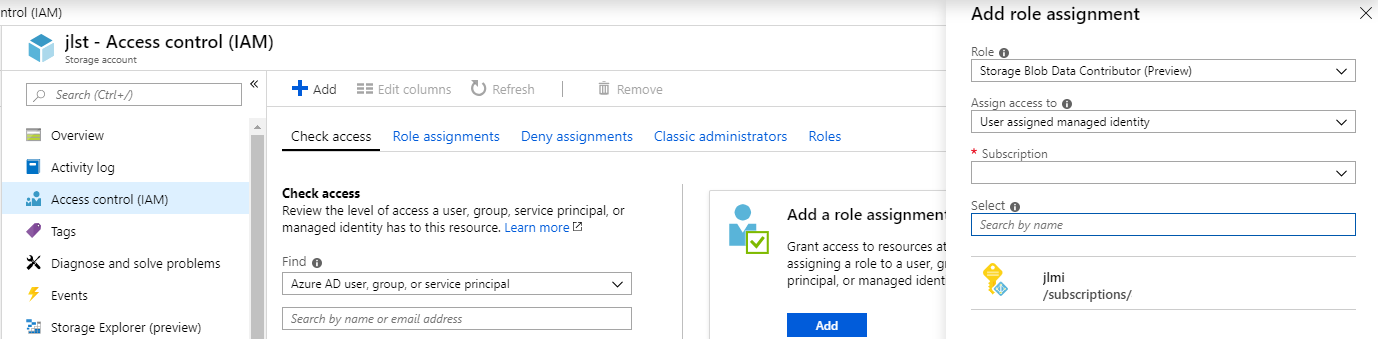
Create resources and grant permissions
Under App Service’s Identity, enable system-assigned identity or user-assigned identity.

Then add it to target resource’s Access control (IAM).
Get access token
System-assigned identity
For system-assigned identity the easiest way is to use AzureServiceTokenProvider.
User-assigned identity
AzureServiceTokenProvider currently doesn’t work with user-assigned identity. Though Connection String doc says RunAs=App;AppId={ClientId of user-assigned identity} is for user-assigned identify, it currently doesn’t work and returns error Connection string RunAs=App;AppId=xxx is not valid. Must contain 'TenantId' attribute and it must not be empty.
To get token for user-assigned identity, we need to use HTTP REST protocol.
C# implementation using HTTP REST protocol
/// <summary>
/// Get managed identity token.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="resource">The AAD resource URI of the resource for which a token should be obtained. </param>
/// <param name="apiversion">The version of the token API to be used. "2017-09-01" is currently the only version supported.</param>
/// <param name="clientId">(Optional) The ID of the user-assigned identity to be used. If omitted, the system-assigned identity is used.</param>
/// <returns>A Bearer token ready to be used with AAD-authenticated REST API calls.</returns>
public static async Task<string> GetToken(string resource, string apiversion, string clientId = null)
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("Secret", Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("MSI_SECRET"));
string url;
if (clientId == null)
{
// Get system-assigned identity token
url = String.Format("{0}?resource={1}&api-version={2}", Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("MSI_ENDPOINT"), resource, apiversion);
}
else
{
// Get user-assigned identity token
url = String.Format("{0}?resource={1}&api-version={2}&clientid={3}", Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("MSI_ENDPOINT"), resource, apiversion, clientId);
}
HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = await client.GetAsync(url);
string content = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
// using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
//JavaScriptSerializer j = new JavaScriptSerializer();
//Dictionary<string, string> list = (Dictionary<string, string>)j.Deserialize(content, typeof(Dictionary<string, string>));
//string accessToken = list["access_token"];
// using using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
var result = JObject.Parse(content);
string accessToken = result["access_token"].ToString();
return accessToken;
}
Sample HttpResponseMessage:
{
"access_token": "eyJ0e...",
"expires_on": "3/21/2019 11:39:40 AM +00:00",
"resource": "https://storage.azure.com/",
"token_type": "Bearer"
}
Then the access token can be used to access resources like Azure Storage.
For example, to use GetToken() in ASP.NET MVC controller:
public async Task<ActionResult> About()
{
var accessToken = await GetToken("https://storage.azure.com/", "2017-09-01", "b5c6a0ef-e0a6-4a01-a95d-a0cdb0223777");
Console.WriteLine(accessToken);
// Create storage credentials from your managed identity access token.
TokenCredential tokenCredential = new TokenCredential(accessToken);
StorageCredentials storageCredentials = new StorageCredentials(tokenCredential);
// Create a block blob using the credentials.
CloudBlockBlob blob = new CloudBlockBlob(new Uri("https://xxx.blob.core.windows.net/xxx/xxx.txt"), storageCredentials);
blob.UploadText("test");
ViewBag.Message = accessToken;
return View();
}
A complete ASP.NET MVC sample Controller
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Auth;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Blob;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
using System;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace mvcmi.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public async Task<ActionResult> About()
{
var accessToken = await GetToken("https://storage.azure.com/", "2017-09-01", "b5c6a0ef-e0a6-4a01-a95d-a0cdb0223777");
Console.WriteLine(accessToken);
// Create storage credentials from your managed identity access token.
TokenCredential tokenCredential = new TokenCredential(accessToken);
StorageCredentials storageCredentials = new StorageCredentials(tokenCredential);
// Create a block blob using the credentials.
CloudBlockBlob blob = new CloudBlockBlob(new Uri("https://jlst.blob.core.windows.net/pic/Blob1.txt"), storageCredentials);
blob.UploadText("test");
ViewBag.Message = accessToken;
return View();
}
/// <summary>
/// Get managed identity token.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="resource">The AAD resource URI of the resource for which a token should be obtained. </param>
/// <param name="apiversion">The version of the token API to be used. "2017-09-01" is currently the only version supported.</param>
/// <param name="clientId">(Optional) The ID of the user-assigned identity to be used. If omitted, the system-assigned identity is used.</param>
/// <returns>A Bearer token ready to be used with AAD-authenticated REST API calls.</returns>
public static async Task<string> GetToken(string resource, string apiversion, string clientId = null)
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("Secret", Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("MSI_SECRET"));
string url;
if (clientId == null)
{
// Get system-assigned identity token
url = String.Format("{0}?resource={1}&api-version={2}", Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("MSI_ENDPOINT"), resource, apiversion);
}
else
{
// Get user-assigned identity token
url = String.Format("{0}?resource={1}&api-version={2}&clientid={3}", Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("MSI_ENDPOINT"), resource, apiversion, clientId);
}
HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = await client.GetAsync(url);
string content = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
var result = JObject.Parse(content);
string accessToken = result["access_token"].ToString();
return accessToken;
}
public ActionResult Contact()
{
ViewBag.Message = "Your contact page.";
return View();
}
}
}